You can use the XLL+ Function Wizard to specify that an argument should contain a vector of a particular type, e.g. a row of strings or a column of dates. This walkthrough demonstrates how to add and use a vector argument in an add-in function.
Creating the project
To create the project using Visual Studio 6
- From the File menu, select New to show the New dialog.
- Select the XLL+ AppWizard 4 project template from the list in the Projects tab, and enter VectorFns in the Project name box. Under Location, enter an appropriate directory in which to create the project.
- Accept all the default settings in both pages of the XLL+ AppWizard.
To create the project using Visual Studio .NET or Visual Studio 2005
- From the File menu, select New and then Project to open the New Project dialog.
- Select the XLL+ Excel Add-in project template from the list of Visual C++ Projects, and enter VectorFns in the Name box. Under Location, enter an appropriate directory in which to create the project.
- Accept all the default settings in the XLL+ AppWizard.
For more details about creating projects, see Creating an add-in project in the XLL+ User Guide.
Creating the function
Use the XLL+ Function Wizard to create a new add-in function and to add a vector argument.
Note: If you do not know how to start the Function Wizard, or you cannot find the tool-bar, look at Installing the Function Wizard under Developer Studio 6 or Installing the Function Wizard under Visual Studio .NET or Visual Studio 2005.
-
Open the source file VectorFns.cpp and click on the New XLL+ Function menu item or tool-button, to show the New Function dialog, and fill in the name, category and description as shown below.
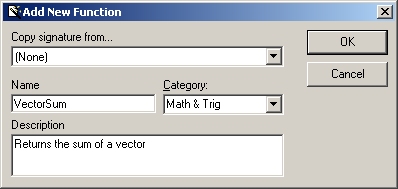
-
Add a new argument named Input of type double, by typing into the arguments grid, as shown below.
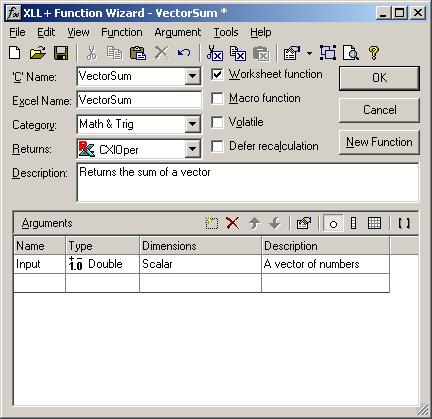
-
Click on the Vector tool, to convert the argument to a vector.
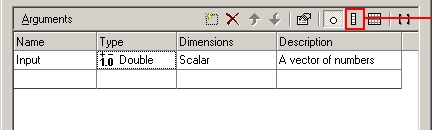
-
The argument is now a vector of type double, as shown below.
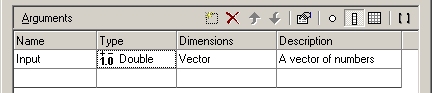
Click on the OK button to close the Function Wizard and save the function.
Inspecting the code
-
The following code has been added to VectorFns.cpp.
extern "C" __declspec( dllexport ) LPXLOPER VectorSum(const COper* Input) { CXlOper xloResult; BOOL bOk = TRUE; std::vector<double> vecInput; bOk = bOk && Input->ReadVector(vecInput, "Input", xloResult); if (!bOk) return xloResult.Ret(); //}}XLP_SRC // TODO - Set the value of xloResult return xloResult.Ret(); }Let us examine the interesting code.
-
Note that the argument has been declared as type COper*. The COper type is usually used to pass vector and matrix values from Excel to add-in functions.
LPXLOPER VectorSum(const COper* Input)
-
A buffer variable vecInput is declared. The contents of the COper argument passed by Excel will be extracted and put into vecInput.
std::vector<double> vecInput;
-
Code has been generated to read the contents of Input into vecInput.
bOk = bOk && Input->ReadVector(vecInput, "Input", xloResult); if (!bOk) return xloResult.Ret();Note that if the cell range passed to the function cannot be read for any reason (for example, because a cell contains a string instead of a number) then an error message will be generated, placed in xloResult, and immediately returned to Excel.
Completing the function
-
Add code to implement the function, as shown below:
extern "C" __declspec( dllexport ) LPXLOPER VectorSum(const COper* Input) { CXlOper xloResult; BOOL bOk = TRUE; std::vector<double> vecInput; bOk = bOk && Input->ReadVector(vecInput, "Input", xloResult); if (!bOk) return xloResult.Ret(); //}}XLP_SRC double dSum = 0.0; for (size_t i = 0; i < vecInput.size(); i++) dSum += vecInput[i]; xloResult = dSum; return xloResult.Ret(); } - Build and test the project.
See Also
Walkthroughs | COper::ReadVector method | Reference: Array arguments